
With house prices staying close to all-time highs, finding a deposit for a house purchase remains a challenge for many buyers. As a result, an increasing number of prospective home buyers are turning to wider family for financial assistance, either to get their first leg up onto the property ladder or move to a larger property to better suit a growing family.
By gifting a deposit, parents can help their children increase the amount they can borrow on a mortgage, in turn enabling them to buy a home which would be impossible without the financial assistance. We have also seen instances where family gifts have been used to reduce an existing mortgage debt, leading to lower monthly mortgage repayments and easing the financial burden.
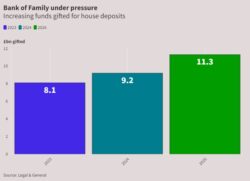
A recent study by Legal & General reported that a total value of £9.2bn will be gifted by parents, grandparents and other family members to help fund house purchases this year, an increase of 13% on the £8.1bn gifted for this purpose in 2023. The same study sees the pace of gifts accelerating, with the amount gifted likely to reach an aggregate of £11.3bn in 2026. Legal & General’s research also showed the average gift made has jumped to £27,400. Similar research from the Centre for Economics and Business Research (CEBR) found that 42% of all property purchased by those aged under 55 this year was in part funded by a gift from family.
Whilst gifting funds is generally well intentioned, parents and grandparents should consider the consequences of their actions before proceeding.
Firstly, any gift made could have potential Inheritance Tax consequences. Each individual can make gifts of £3,000 per Tax Year and therefore a married couple could gift £6,000 of capital (plus £3,000 each from the previous Tax Year if not used) without any Inheritance Tax concerns. As highlighted by the Legal & General research, this is some way short of the average amount of financial help provided. Any amount gifted above the gift exemption is treated as a Potentially Exempt Transfer (PET). No Inheritance Tax is due immediately; however, the person making the gift needs to live seven years from the date the gift is made, for the gift to fully escape Inheritance Tax.
Parents and grandparents also need to be aware that a gift is absolute. If the child buys a property jointly with an unmarried partner, the consequences of relationship breakdown could mean that “family wealth” is unprotected, if the property is later sold. Unfortunately, this is a common occurrence, and all parties involved should seek specialist legal advice to determine how gifted deposits are dealt with.
Some parents might consider co-ownership with their children, as an alternative to gifting funds outright. This needs very careful thought, as this option is likely to incur an additional Stamp Duty levy, if the parent already owns a property. Further complications could also arise if the parents need to release funds from the property at some point in the future.
Parents and grandparents making gifts need to carefully consider their own financial requirements before taking any action. The Legal & General research shows that 40% of those gifting deposits are using cash savings and investments to fund the gift, and 12% are accessing pension savings for this purpose. As a result, many older family members gifting money are financially less secure after making the gift.
Most calls to the “Bank of Mum and Dad” are when parents are typically in their 50s or 60s. This is a time when parents should be concentrating on their retirement plans, and gifting funds at this time can not only mean that cash or investments are unavailable to cover unexpected expenditure, but also affect their income in retirement.
Parents typically want to ensure that their children are treated equally, and this could lead to added financial pressure. Gifting funds to one child, for example, may increase the expectation that a similar gift is also made to other children in the future. This could be at a time when available funds are limited or being used to fund retirement.
Given the findings of the Legal & General survey, and our own experience of advising clients in this situation, it would be wise to think ahead and begin putting aside funds to give children a helping hand onto the property ladder. One option is to fund the child’s Junior Individual Savings Account (ISA) with regular contributions over time. It is important to note that the returns achieved on the underlying cash or investments within the Junior ISA will dictate the amount available to the child, and therefore careful consideration needs to be given in respect of the choice of investment. The other risk with a Junior ISA is that the account can be accessed when the child turns 18, which may well be too early for the funds to be used for its intended purpose. An alternative is to place funds in a separate investment portfolio, where the parent or grandparent can keep control of the funds. This could be arranged in a tax-efficient manner, for example, by using an Investment Bond.
We strongly recommend that parents and other family members, faced with calls on the generosity of the “Bank of Family”, take advice, as there are a number of financial and legal considerations that need careful consideration. At MGFP, we regularly are called on to provide such advice to parents and grandparents, including the most appropriate method of funding the gift, and the potential financial impact of any actions taken on their financial security. We can also provide advice on appropriate investment solutions where parents and grandparents can regularly save to build a capital sum for their children or grandchildren’s future. Speak to one of our experienced financial planners for independent and expert advice.